
There’s been a flourishing of data centres across all continents. Rising dependence on cloud technologies, AI, IoT, 5G, and big data to facilitate everyday life and ensure business continuity has increased the number and size of server rooms around the globe. Ever greater dependence on these technologies means that unexpected downtime at any data centre can have significant consequences for the individuals, businesses, and organisations that rely on them. Furthermore, unscheduled halts can cause serious reputational and economic damage to the companies that own data centres. Still, with so much electrical, electronic, and mechanical infrastructure under one roof, it can be difficult to maintain the health of server rooms. Thankfully, thermal imaging cameras and IR windows offer an efficient, easy, and effective solution to spotting potential problems before they become catastrophic faults.[1]
Quick Links
- What is Thermal Imaging?
- Why are Thermal Cameras Key to Data Centre Maintenance?
- How can Thermal Imaging Improve Data Centre Maintenance?
- Which FLIR Thermal Cameras are Suitable for Data Centre Maintenance?
- Further Information
What is Thermal Imaging?
Thermal imaging detects infrared (IR) energy and converts it into a visible image. Infrared radiation or heat exists between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. All objects above absolute zero, whether living or inanimate, emit infrared radiation. This includes things like ice cubes. Thermal cameras are fitted with detectors that pick up these wavelengths and include technology that turns them into a visual image. These images are coloured using a thermal palette, which indicates the heat distribution across a scene. As such, you can clearly and easily see the hottest (usually indicated by yellow or white) and coldest (typically displayed in blue or dark purple) points in an area. This is especially useful for detecting heat anomalies. For example, overheating components may be in danger of failing, while cold parts might have already broken.
Why are Thermal Cameras Key to Data Centre Maintenance?
It is undeniable that infrared thermometers, like thermal cameras, provide a non-contact, simple method of measuring temperatures. Similarly, it is impossible to dispute that most IR thermometers are significantly cheaper than even the most basic of thermal cameras. However, IR thermometers can only ascertain the temperature of one small area at a time and will only provide you with a numerical measurement.
Conversely, a thermal camera can capture infrared images of notably larger areas and will provide a temperature reading for each pixel (model dependent). As such, although a thermal camera requires a greater initial investment, the return on investment will also be greater. In choosing a thermal camera, specifically a FLIR thermal camera, you will benefit from the following.
Comprehensive Coverage
Like IR thermometers, thermal cameras can find hot spots or temperature differences. Unlike IR thermometers, thermal cameras make identifying these potential problems, regardless of size, easy, requiring minimal effort on the part of the engineer. That’s because, whereas IR thermometers can only take the temperature of a specific spot, thermal cameras can capture images and footage of larger areas. Furthermore, thermal differences between components are clearly indicated by the thermal palette, allowing engineers to see impending faults and compare temperatures immediately on the screen. As a result, tasks that, when conducted using an IR thermometer, would require meticulous temperature documentation and comparison, take just moments with a thermal camera. Consequently, you can easily, efficiently, and accurately assess entire electrical installations, buildings, and HVAC installations.
Quick Inspections
In addition to this, as thermal cameras capture and measure large areas from a safe distance, maintenance engineers can complete inspections faster than previously possible.
Maximised Uptime
As mentioned, thermal cameras allow engineers to conduct inspections quickly and accurately from a safe distance. This means data centres no longer need to shut down for routine maintenance checks. Consequently, not only are potential problems identified before they become catastrophic, but costly inspection downtime is not incurred, thereby saving companies money on two fronts.
Streamlined Reporting
Thermal cameras also offer the advantage of streamlined, insightful, professional reporting. Using a compatible desktop software or app, technicians and engineers can compare current inspection data with historical information to identify trends and make informed conclusions/decisions. Thermal reporting programs often include report templates, making report creation easier. Moreover, batch processing and image-editing functions streamline analysis and reporting.
Additionally, some thermal software will facilitate route planning. Staff can design maintenance routes in the program, which are then uploaded to compatible thermal cameras. This means that regardless of which colleague uses the imager to conduct the inspection, the correct data will be gathered.
How Can Thermal Imaging Improve Data Centre Maintenance?
As previously mentioned, data centres include an array of electrical, electronic, and mechanical infrastructure. Thermal imaging cameras can detect faults early in all this equipment while operations are ongoing. Below are some of the ways thermal imaging cameras can improve data centre maintenance inspections.
Assess Electrical & Mechanical Systems
Increased heat in electrical components is usually a precursor to failure. FLIR explains that heat is generated when a current passes through a resistive element. This is normal for electrical connections. However, when these connections corrode or loosen, their resistance increases, which, in turn, causes even more heat to be generated. This temperature rise can cause components to fail. Similarly, load imbalances and impedance increases may result in temperature rises and component failures.
Thankfully, thermal imaging allows maintenance technicians to identify hot spots and determine the severity of the problem. This data facilitates effective repair prioritisation, helping data centres avoid catastrophic downtime. Thermal cameras can be used to find issues with:
- Overheating connections
- Overloaded or imbalanced circuits
- Damaged switches
- Faulty fuses
- Power supplies
- Battery systems
- Generator systems
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Transformers
- Electrical panels
- Resistive load banks
Monitor HVAC & Cooling Infrastructure
To maintain optimum operation, data centres utilise a hot aisle/cold aisle layout. Server racks are lined up with the front sides facing each other. These corridors are the cold aisles, cooled by the Computer Room Air-Conditioning (CRAC) unit at the bottom of a raised floor. Predictably, the backs of the servers also face each other and are arranged down hot aisles, so called because the backs of the servers vent out hot air into these corridors. This hot air is then recycled through the CRAC to cool the cold aisles.
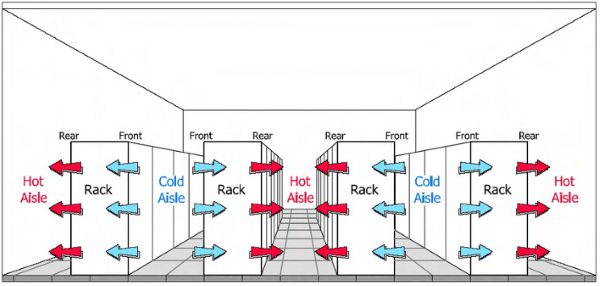
It is important to maintain this hot-aisle-cold-aisle arrangement as our increasing reliance on web-based technology means data centres must condense more servers into their racks. Thermal imaging cameras can help to maintain this setup and, thereby, ensure the health of data centres. This is because they can help maintenance engineers to:
- Monitor server rack temperature
- Spot misaligned ductwork and/or leaking ducts
- See electrical or mechanical faults within CRAC units
- Pinpoint sources of energy loss
- Find missing insulation
- Locate AC condensate leaks
- Identify inoperable or damaged internal server fans
Protect Renewable Energy Sources
Running a data centre is energy intensive. As we transition to Net Zero, more data centres will be turning to sources of renewable energy, such as solar and wind power, to fuel their operations. Thermal imaging cameras will play an integral role in maintaining renewable energy sources and, therefore, the continued operation of data centres.
Solar Power
Like most things, solar panels are susceptible to wear, which can weaken their ability to capture energy and distribute electricity. Fortunately, thermal cameras can be used during normal operation to scan solar/photovoltaic (PV) panels and identify potential issues down to a cellular level. Thermal imaging cameras offer the advantage of scanning large areas quickly, making them the perfect tools for efficiently assessing PV panels whether they are installed on rooftops or in solar farms.
Wind Power
Similarly, wind turbines also contain components that can wear and break. Thermal imaging cameras offer the unique advantage of inspecting all the electrical and mechanical components of wind turbines and the connected electrical system during uptime. As such, maintenance engineers can pinpoint potential problems before breakdown occurs.
Prevent Fires
Data centre fires are unusual. Nevertheless, when they do ignite, they can have a crippling effect on server rooms, destroying many assets and halting service, leading to both economic and reputational damage. Thermal cameras can identify potentially incendiary hotspots early, enabling teams to address them before they spark a fire. It is important to note that while thermal cameras are not a replacement for fire alarms and sprinkler/firefighting systems, they can significantly reduce the activation of these systems.
Ensure Security
In addition to detecting mechanical and electrical hotspots, thermal cameras can also identify body heat, making them ideal for 24/7 data centre security applications. Offering high contrast, high resolution, and long detection ranges, thermal imaging cameras can spot potential intruders or trespassers in adverse conditions such as rain, fog, smoke, or total darkness. What’s more, when paired with video analytics, radar and/or HD visible cameras, the likelihood of false positives is reduced while alarm verification and intruder identification is improved.
Which FLIR Thermal Cameras are Suitable for Data Centre Maintenance?
FLIR offers several thermal camera models suitable for inspecting and/or monitoring data centres, including the FLIR Ax8 Thermal Camera, FLIR A40 Advanced Smart Sensor Thermal Camera, and FLIR Exx-Series Thermal Cameras.
FLIR Ax8 Thermal Camera

The FLIR Ax8 Thermal Camera provides continuous temperature monitoring and imaging, thereby preventing mechanical and electrical failures as well as potential fires. This compact, affordable IR Imager is easy to install.
- IR resolution: 80 x 60px
- Thermal sensitivity: 100mK
- FOV: 48° x 37°
- 640 x 480px digital camera
- MSX imaging
- Temperature range: -10°C to +150°C
- 6 spotmeters
- 6 area boxes
- Automatic hot/cold detection
- Measurement presets
- Alarm functions (max of 5 alarms)
- Ethernet control and image streaming
- Ethernet protocol compatibility
FLIR A40 Advanced Smart Sensor Thermal Camera

Offering built-in analytics and alarm capabilities, the FLIR A40 Advanced Smart Sensor Thermal Camera is ideal for condition monitoring and early fire detection. As such, the FLIR A40 Thermal Camera is perfect for protecting data centre assets, improving server room safety, maintaining uptime, and reducing maintenance costs.
Buy FLIR A40 Advanced Smart Sensor Thermal Camera
- Easy integration into IT systems with support for industrial protocols such as Modbus TCP, EtherNet/IP, MQTT, and REST API
- Small and rugged with M8/12 Ethernet, Digital I/O, and RS-232/485 connections
- IP66
- Diamond-like carbon coating on the lens
- On-camera analytics and alarms
- IR resolution: 320 x 240px
- Temperature accuracy: ±2°C
- Low-noise imagery and data
- MSX imaging
- Easy HMI and SCADA integration
- SNMP trap and advanced firewall protection allow multiple network devices to operate securely together
- Simple configuration via a standard web browser
- Simultaneous VMS video and alarm integration ONVIF S compatibility
- Compact
- Lightweight
- Multiple mounting options
- Available with 29°, 51°, and 95° lenses
FLIR Exx-Series Thermal Cameras
The FLIR Exx-Series Thermal Cameras are handheld IR imagers suitable for inspecting electrical, mechanical, and HVAC equipment in data centres. Ideal for routine maintenance checks, FLIR’s Exx-Series Thermal Cameras are perfect for detecting impending faults to prevent unexpected downtime.

Teledyne FLIR E52 Thermal Camera
- 24° lens
- IR Res: 240 x 180px
- Thermal sensitivity: 50mk
- Temperature range: up to 550°C
- Accuracy: ±2°C/2%
- 5MP visual camera
- 640 x 480px touchscreen
- Radiometric imaging
- Spotmeters
- 1-touch level/span
- MSX imaging
- 1-4x digital zoom
- Manual focus
- GPS
- Voice annotation
- MeterLINK
- USB, Bluetooth, & Wi-Fi
- Automatically uploads images to the FLIR Ignite Cloud
- Inspection Route technology

Teledyne FLIR E54 Thermal Camera
- 24° lens
- IR Res: 320 x 240px
- Thermal sensitivity: 40mk
- Temperature range: up to 650°C
- Accuracy: ±2°C/2%
- 5MP visual camera
- 640 x 480px touchscreen
- Radiometric imaging
- Spotmeters
- 1-touch level/span
- MSX imaging
- 1-4x digital zoom
- Manual focus
- GPS
- Voice annotation
- MeterLINK
- USB, Bluetooth, & Wi-Fi
- Automatically uploads images to the FLIR Ignite Cloud
- Inspection Route technology
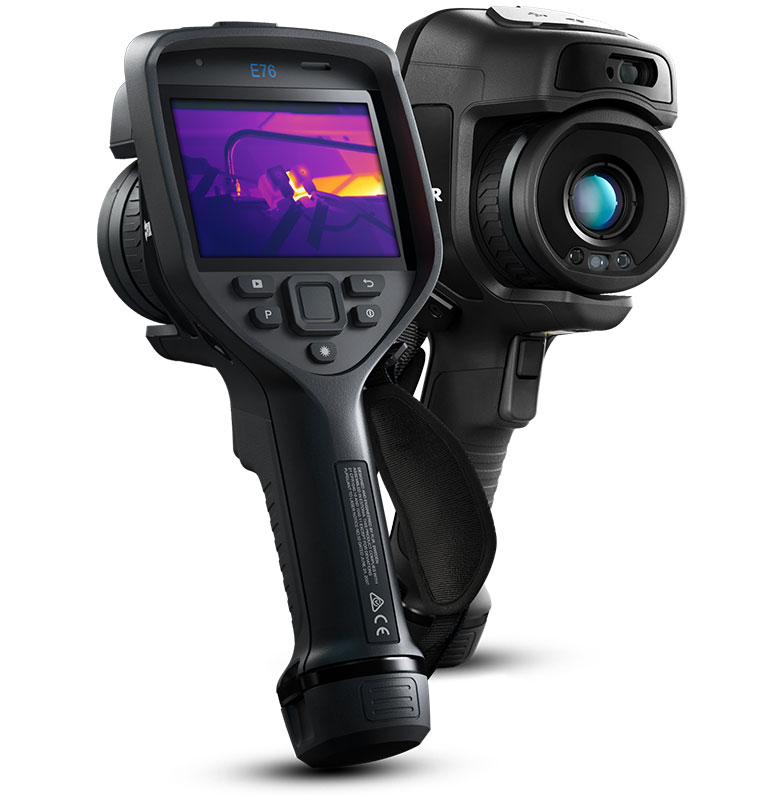

Teledyne FLIR E76 Thermal Camera
- Choice of lens (14°, 24°, 42°, 80°, and 14°- 24° FLIR FlexView™)
- IR Res: 320 x 240px
- Thermal sensitivity: 30mk
- Temperature range: up to 650°C
- Accuracy: ±2°C/2%
- 5MP visual camera
- 640 x 480px touchscreen
- Radiometric imaging
- Spotmeters
- 1-touch level/span
- MSX imaging
- UltraMax
- 1-4x digital zoom
- Automatic, laser, & manual focus
- GPS
- Voice annotation
- MeterLINK
- USB, Bluetooth, & Wi-Fi
- Automatically uploads images to the FLIR Ignite Cloud
- Inspection Route technology
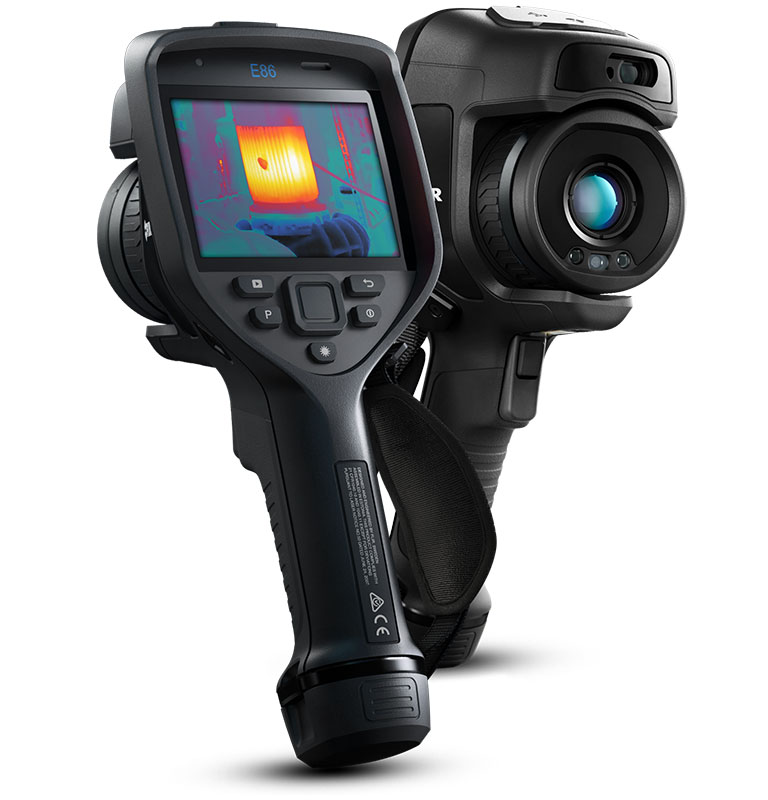

Teledyne FLIR E86 Thermal Camera
- Choice of lens (14°, 24°, 42°, 80°, and 14°- 24° FLIR FlexView™)
- IR Res: 464 x 348px
- Thermal sensitivity: 30mk
- Temperature range: up to 1500°C
- Accuracy: ±2°C/2%
- 5MP visual camera
- 640 x 480px touchscreen
- Radiometric imaging
- Spotmeters
- 1-touch level/span
- MSX imaging
- UltraMax
- 1-6x digital zoom
- Automatic, laser, & manual focus
- GPS
- Voice annotation
- MeterLINK
- USB, Bluetooth, & Wi-Fi
- Automatically uploads images to the FLIR Ignite Cloud
- Inspection Route technology
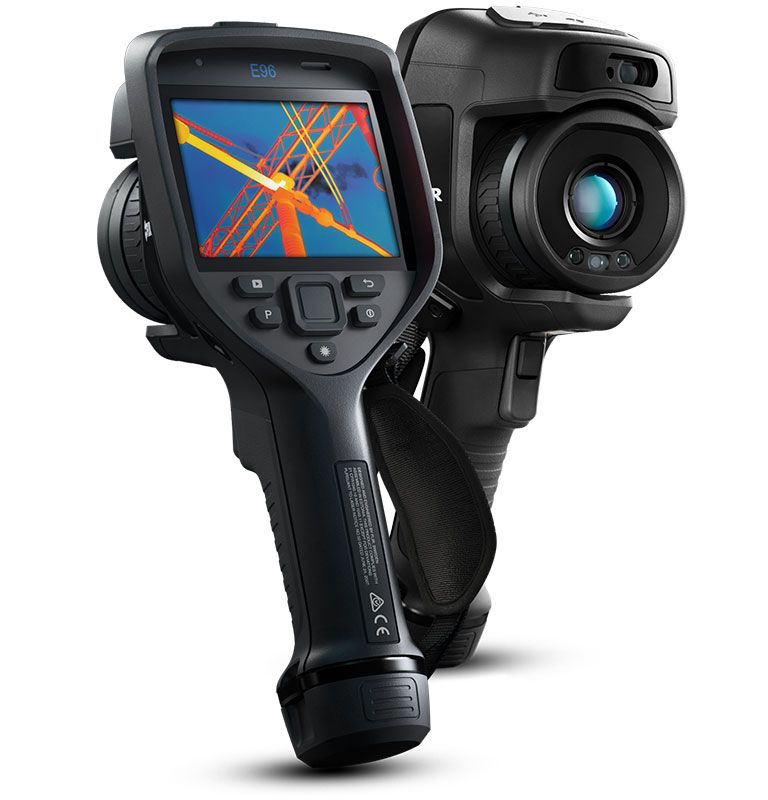

Teledyne FLIR E96 Thermal Camera
- Choice of lens (14°, 24°, 42°, 80°, and 14°- 24° FLIR FlexView™)
- IR Res: 640 x 480px
- Thermal sensitivity: 30mk
- Temperature range: up to 1500°C
- Accuracy: ±2°C/2%
- 5MP visual camera
- 640 x 480px touchscreen
- Radiometric imaging
- Spotmeters
- 1-touch level/span
- MSX imaging
- UltraMax
- 1-8x digital zoom
- Automatic, laser, & manual focus
- GPS
- Voice annotation
- MeterLINK
- USB, Bluetooth, & Wi-Fi
- Automatically uploads images to the FLIR Ignite Cloud
- Inspection Route technology
What are IR windows?
IR windows offer a barrier between the maintenance engineer and the energised equipment being inspected, protecting both the individual and the infrastructure. In high voltage environments, IR windows prevent arc flash injury while ensuring compliance with NFPA 70E requirements.
In regards to data centres, IR windows provide insight into the functionality of server racks, allowing maintenance technicians to spot overheating components as well as assess heat distribution across the aisles.
FLIR offers IRW Infrared Windows in various sizes. These easy-to-install IR windows are compatible with all FLIR’s infrared cameras, including the aforementioned Exx-series, A40, and Ax8 Thermal Cameras.
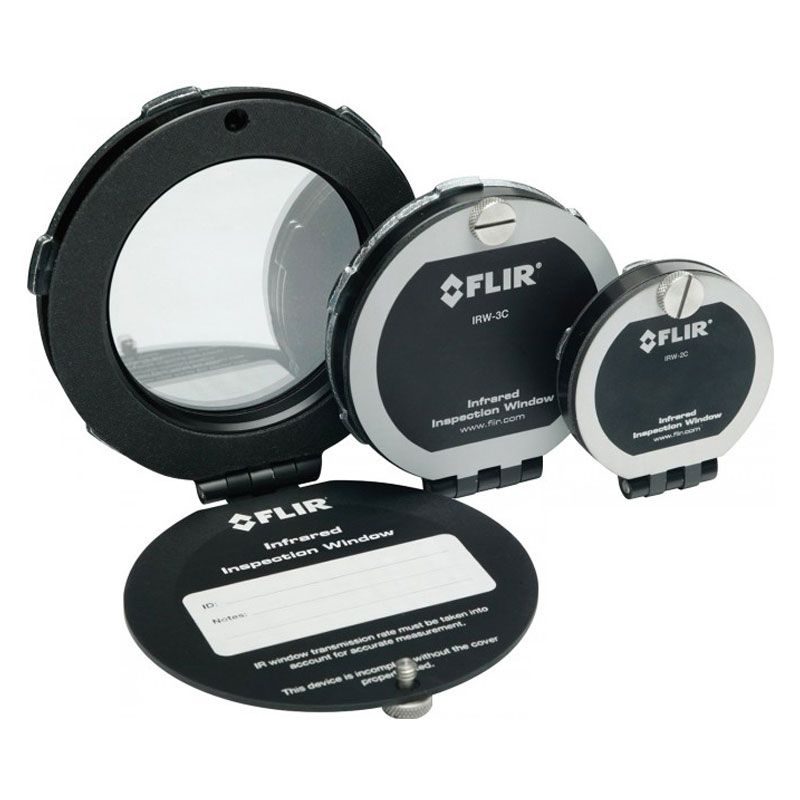

- Easy to install: one hole required with PIRma-Lock ring nut to tighten
- PIRma-Lock reliability: teeth lock tight to inside of the panel with automatic metal component grounding
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor electrical panel installation
- Broadband crystal IR window lets through radiometric images
- Compatible with all FLIR thermal cameras
- Selection of sizes available
Further Information
For more help or advice regarding FLIR’s thermal cameras and IR windows for data centres, please contact our Sales team on 01642 931329 or via our online form.
Alternatively, you can read more about Defending Data Centres Using Teledyne FLIR Thermal Imaging here.
In the meantime, please browse our extensive range of FLIR IR windows and thermal cameras at tester.co.uk
Footnotes
[1] Information about using thermal cameras in data centres was gathered from the following sources:
- Teledyne FLIR, Thermal Imaging for Data Centres, last accessed 07 April 2024.
- Teledyne FLIR, Technical Note: Thermal Imaging for Data Centres, last accessed 07 April 2024.


